Rubber has been utilized by humankind for over 1,000 years and has become a noteworthy commodity of interest in the world of investments. People find a wide array of uses for rubber like rubber roofs, rubber mats, rubber gloves, and even rubber ducks.
In the year 2022 alone, Statista reported that the global usage of rubber amounted to approximately 14.2 million metric tons of natural rubber and 15.4 million metric tons of synthetic rubber. This illustrates its widespread applications.
According to a report from Globe News Wire, the rubber market is poised for substantial growth, with a projected annual rate of 6%, expected to reach a valuation of USD $73.42 billion by 2029. Notably, China stands as the world’s largest consumer of natural rubber, extensively employing it in various manufacturing processes, including the production of automobiles and tires.
Given China’s pivotal role in the rubber market, Rubber Futures on the Shanghai International Energy Exchange (INE) have garnered immense popularity among investors. In this article, we aim to explore 4 important factors when trading INE Rubber Futures.
Click here to find out the 6 Things to Take Note When Trading Rubber Futures.

Where are Rubber Futures Traded?
Traders can trade Rubber Futures from Singapore Exchange (SGX) and Shanghai International Energy Exchange (INE) through Orient Futures International Singapore.
Orient Futures is a futures trading Singapore company and is an indirect subsidiary of Shanghai Orient Futures. INE offers TSR20 Rubber Futures contract for traders to trade in, whereas SGX offers both SICOM RSS3 and SICOM TSR20 SGX Rubber Futures.
To trade Rubber Futures on INE, international traders need to go through an overseas intermediary like Orient Futures International Singapore, using either the QFI China Scheme or China’s list of internationalized products.
INE Shanghai Rubber Futures Contract Specifications
The INE Rubber Futures Contract has the following specifications:
The INE Rubber Futures Contract has a minimum price fluctuation of CNY 5/metric ton.
Contract months are monthly all year round.
The last trading day of the contract month is the 15th trading day of the delivery month.
The INE trading hours are from Monday to Friday, at these trading hours:
9:00 am – 11:30 am, 1:30 pm – 3:00 pm (Beijing time)
INE TSR20 Rubber Futures symbol: NR

4 Important Factors When Trading INE China Rubber Futures
1. China's Dominance in Rubber Production and Consumption
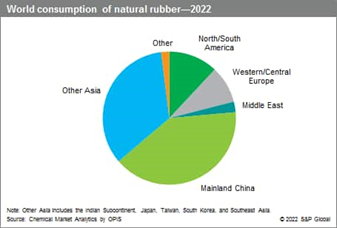
According to the Rubber Market Size & Analysis Report by Mordor Intelligence, China is the world’s largest importer and consumer of natural rubber, accounting for approximately 40.0% of the total global output annually.
As one of the major three automobile manufacturers in the world, China’s increasing growth in the automobile industry has resulted in a heightened demand for raw materials in recent years, such as the demand for natural rubber. Therefore, the rising demand for latex products, coupled with the growing global automobile and construction industries, is one of the major factors anticipated to drive the natural rubber market in the coming years.
According to Statista, China consumed a total of around 5.7 million metric tons of Rubber in 2022. This was followed by India and the United States, which consumed 1.3 million metric tons and one million metric tons of natural rubber that year, respectively.
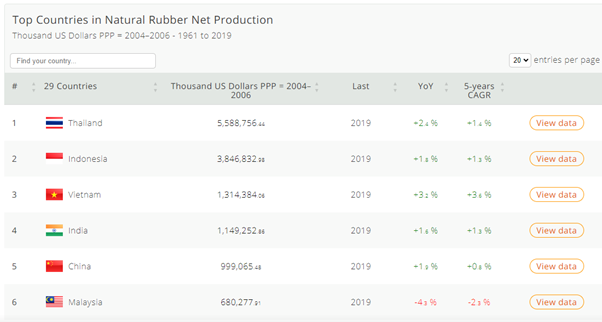
Although China is not the largest producer of rubber in the world, it is one of the top few largest producers of rubber. According to Nation Master, Thailand is the largest natural rubber producer globally, with China also being one of the key players, contributing a significant portion to the world’s natural rubber production.
China’s position as the largest rubber consumer and a major producer makes trading INE rubber futures a strategic option for traders. China’s enormous demand drives global prices, while its substantial production reinforces its influence.
2. Global Economic Growth and Automotive Industry
The demand for rubber is closely linked to a country’s economic growth and the automotive industry.
With China reopening its market to the world and the rapid expansion of its automotive sector, the demand for tires and other rubber products is on the rise. According to Reuters, China’s overall auto sales are expected to grow by 3% this year to reach 24.9 million vehicles, recovering to pre-COVID-19 levels. They forecast growth to 30.6 million vehicles by 2030.
Given China’s emphasis on producing Electric Vehicles (EVs), the increased demand for rubber is expected to surge even further.
Furthermore, Trading Economics also reported that both industrial activity and retail sales of rubber in China exceeded expectations in August this year.
3. Currency Exchange Rates
Exchange rate fluctuations can exert a significant influence on the prices of rubber futures, especially when trading in currencies other than the Chinese yuan (CNY). Currency movements can either amplify or mitigate the impact of price changes in the rubber futures market. For instance, if you’re trading rubber futures in US dollars (USD) as an investor from outside China, shifts in the CNY-USD exchange rate can directly affect the value of your investment. A strengthening CNY relative to the USD could potentially erode the value of your rubber futures position when converted back to your base currency, whereas a weakening CNY could have the opposite effect.
4. Rubber Cross-Arbitrage
Traders can also look to do Rubber Cross-Arbitrage with INE China Rubber Futures.
Rubber cross-arbitrage is a trading strategy that capitalizes on price disparities between rubber futures contracts on different exchanges. Since Rubber Futures are traded on both the Shanghai International Energy Exchange (INE) and the Singapore Exchange (SGX), traders can leverage these price differences to maximize their returns and minimize risks.
By simultaneously buying rubber futures contracts on the exchange with the lower price and selling them on the exchange with the higher price, traders can exploit these discrepancies, profiting from market inefficiencies. This strategy also contributes to market stability and price convergence, benefiting both traders and the overall market.
The arbitrage strategy can also be applied to other commodities and forex futures, such as Copper Arbitrage, and more.
Start Trading with Orient Futures Singapore
Being an Overseas Intermediary of Shanghai International Energy Exchange (INE), Dalian Commodity Exchange (DCE), and Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange (ZCE), when foreign clients participate in internationalised futures contracts in these Chinese markets with us, they have direct access to trading, clearing, and settlement. Our parent company, Shanghai Orient Futures, is the largest broker in terms of aggregated volume across the five regulated exchanges in China.
Orient Futures Singapore also currently holds memberships at the Singapore Exchange (SGX), Asia Pacific Exchange (APEX), and ICE Futures Singapore (ICE SG). Starting August 2023, corporate clients can also gain access to the B3 Exchange through us.
We provide bespoke services to our professional clients, tailored to their corporate and individual needs. Our team will be there for you 24 hours on trading days to provide a one-stop portal for all your trades, with simple processes and an intuitive user interface that has low or near-to-zero latency.



