What Is Arbitrage?
Arbitrage is the simultaneous purchase and sale of the same asset in a different market. It is commonly used by institutional and professional traders as part of a trading strategy.
Cross Border Arbitrage Trade
Cross Border Arbitrageurs can make risk-free profits, which makes it one of the most attractive strategies amidst the fast-paced market environment. For example, cross-border commodity arbitrage can occur when there is a price difference in the different futures exchange markets, buyers can then simultaneously buy low and sell high.
While cross-border arbitrage is described as risk-free, that only applies in theory, in reality, buy and sell techniques that are defined as “low-risk” arbitrage can quickly become “high risk” if one is not careful and trades without a robust risk management system.
To understand more about arbitrages in the market, this article will elaborate on arbitrage opportunities in the recently expanded QFI regime from China on 2nd Sept.
Why Cross-Arbitrage?
Cross Arbitrage is diverse and is used not only in commodity trading but also used in currency, indices, and fixed-income forms of trading.
Being able to use the same strategy as a form of hedge or price discovery mechanism among the different markets makes it an important reason to participate in it.
Moreover, arbitrageurs are placed in a position to gain profits from vast movements and price changes amidst socio-economic circumstances such as the volatile environment from geopolitical changes, or an increase in interest rate from FED by three-quarters of a percentage point.
Ideally, cross-arbitrage provides a good trading opportunity, and seeking contracts with similar maturity will smoothen the trading process.
What Is an Example of Arbitrage or Cross-Arbitrage?
In a recent webinar, Marcus Goi, CEO of Orient Futures Singapore provided a simple example of an arbitrage of LME against China products, from US dollars to RMB. More examples of such arbitrage opportunities are also mentioned amongst different pairings from Chinese exchanges as shown in the comparison table below:
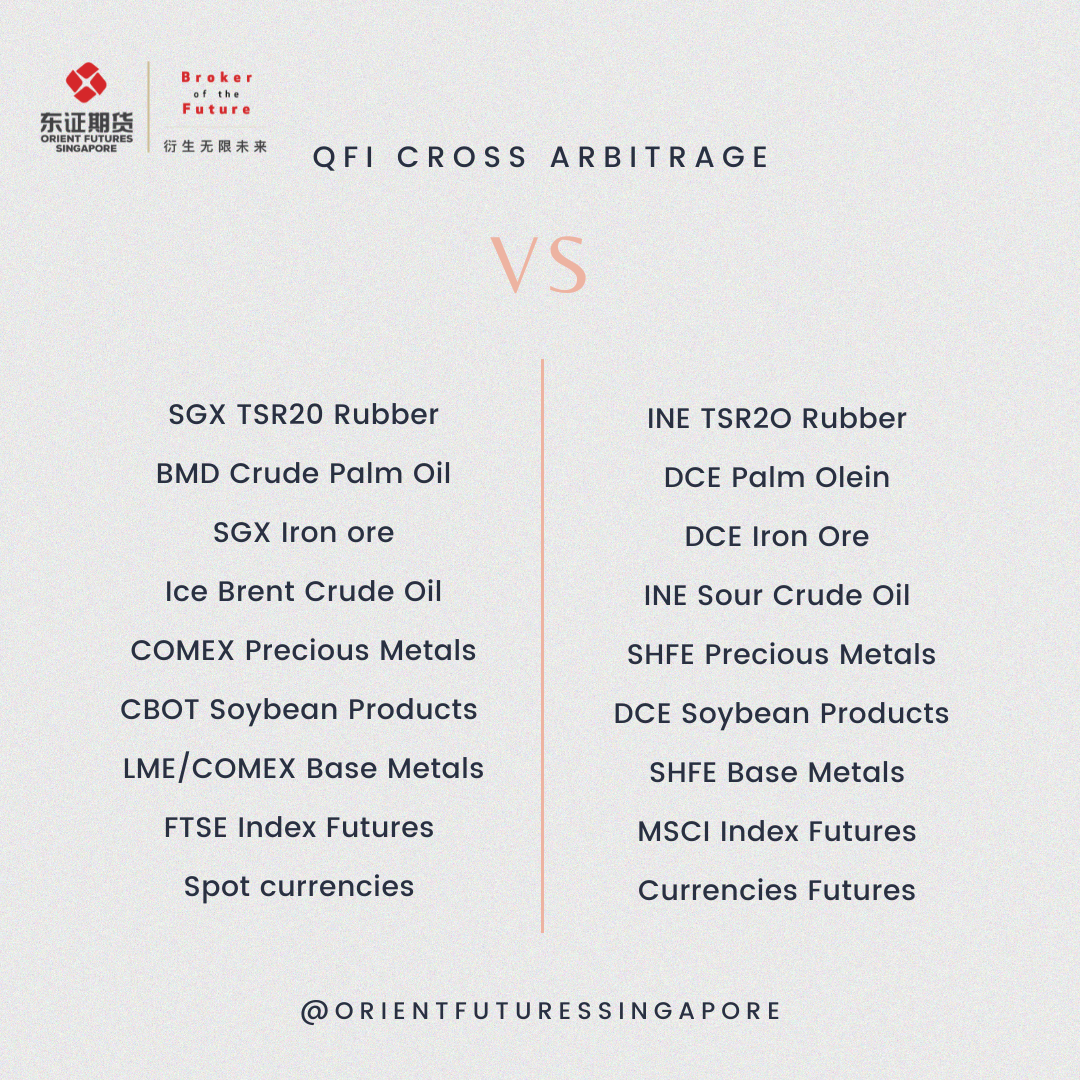

How Do You Make Money from Arbitrage?
Making money from arbitrage is done by taking advantage of the price difference between two or more markets. However, when executing strategies such as a long and a short, variables such as the fluctuating PNL can cause disruptions.
Therefore, instead of a daily conversion of currencies, Orient Futures Singapore shortens the process through a multi-currency single account. Through the single account, multi-currency mechanism, the duty of conversions across currencies is managed by the broker instead of the clients.
Another benefit of trading with the company is that the company prioritizes the client’s benefits by ensuring that interest cost should be lower than FX risk, to achieve that, Orient Futures Singapore does not convert any client’s currency deficit back into its base currency unnecessarily.
Overall, the low latency, single platform account mitigates execution risks such as slippages, largely reducing problems while protecting profits.
To start trading today, open an account with Orient Futures Singapore or contact us here.
Is QFI Arbitrage a Good Investment?
Engaging in any form of arbitrage trading can be a good investment under two conditions:
- A well-developed infrastructure.
- Adequate liquidity management.
On one hand, a well-developed infrastructure will allow professional and institutional traders to keep up with changes and react accordingly. This includes the use of correct online trading platforms such as CQG, TT, Stellar, ATP, MT5, and Maxx Trader. Other factors such as accurate real-time indicators and technical analysis tools are also integral to a good trading system.
On the other hand, liquidity management is paramount for a smooth trade process. In this case, choosing the correct brokerage firm will allow the firm to perform liquidity management in place of clients. For example, being able to offset the profit and loss (PNL) between what is gained at one exchange and what is lost in another exchange without additional intervention from the client’s end is good liquidity management.
An investment made on the foundation of these two factors together with the diversity of products can help make the QFI a good investment.
How Do I Become A QFII?
To become a QFII, traders would have to apply for a license from the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) and then file for an investment quota at the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE).
Additional information regarding the QFI scheme is also available in the following articles:
1) 5 things to know about the QFI scheme,
2) Opportunities with the latest QFII and RQFII policy changes,
3) Implication of QFII and RQFII changes – Easier market access and streamlined processes
To apply for a QFII license, clients can also contact us and our specialist team will be able to guide you to access China’s capital markets.
Cross Border Market Outlook
The market outlook is now largely affected by 5 main factors:
- Geo-political uncertainties
- Disruption of the supply chain
- Monetary policies differences
- Implementing rules to protect domestic markets
- Regulation differences and restrictions
Start Trading With Orient Futures Singapore
Being an Overseas Intermediary of Shanghai International Energy Exchange (INE), Dalian Commodity Exchange (DCE), and Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange (ZCE), when foreign clients participate in internationalised futures contracts in these Chinese markets with us, they have direct access to trading, clearing, and settlement. Our parent company, Shanghai Orient Futures, is the largest broker in terms of aggregated volume across the five regulated exchanges in China.
Orient Futures Singapore also currently holds memberships at the Singapore Exchange (SGX), Asia Pacific Exchange (APEX), and ICE Futures Singapore (ICE SG).
We provide premium customer service at an affordable cost to all our clients. Our team will be there for you 24 hours on trading days to provide a one-stop portal for all your trades, with simple processes and an intuitive user interface that has low or near-to-zero latency.





